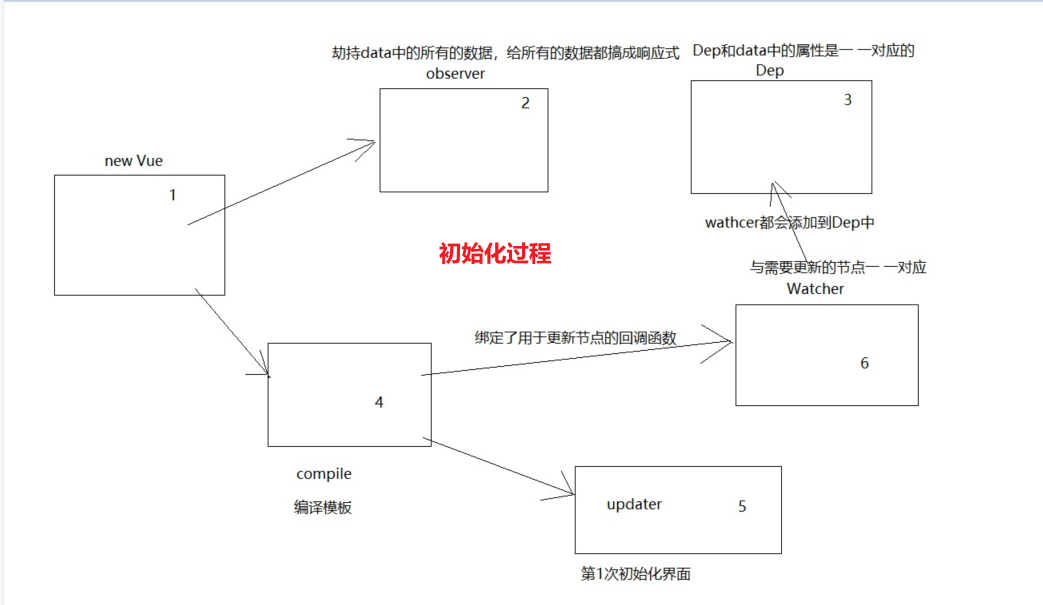
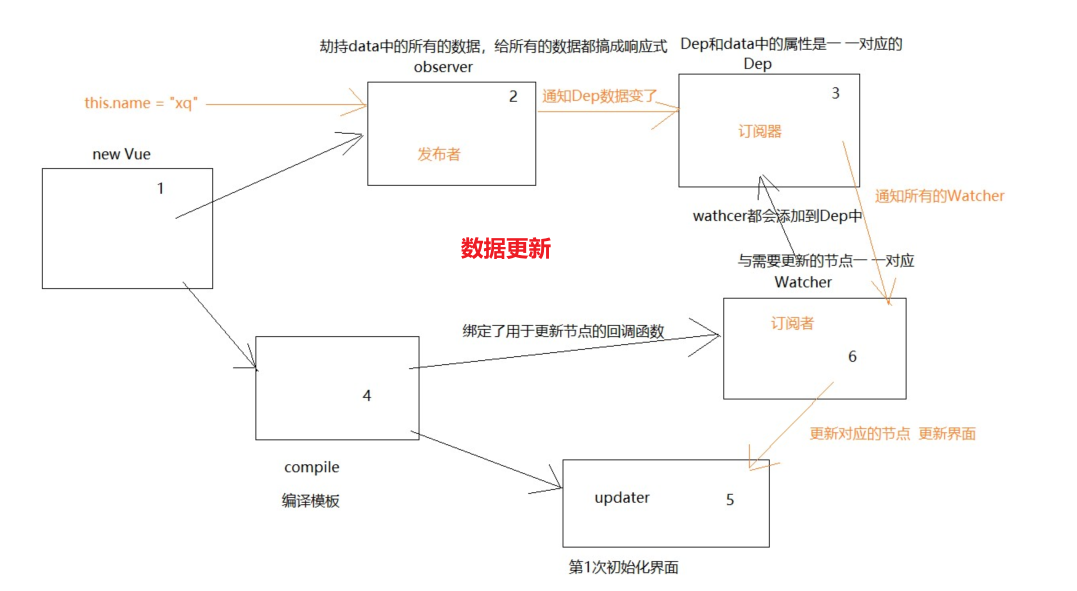
01-手写MVVM
码路教育 12/12/2022
# 一,铺垫
# 1,初步了解Vue2.x响应式原理
响应式网站:随着设备屏幕的变化,网站会加载不同的CSS,展示出不同的效果。
响应式数据:当获取数据和修改数据时,需要感知到数据变了,需要重新渲染视图。
<!-- <script>
// let data = {
// // msg并不是响应式的
// msg:"hello malu"
// };
let vm = {};
Object.defineProperty(vm,"msg",{
enumerable:true, // 可枚举(可遍历)
configurable:false, // 不可删除,不可配置
// 当获取msg走get
get(){
console.log("get...");
return "hello malu"
},
// 当修改msg走set
set(val){
console.log("set...",val);
}
})
</script> -->
<!-- <div id="app">hello</div>
<script>
let data = {
msg:"hello malu"
};
let vm = {};
Object.defineProperty(vm, "msg", {
enumerable: true,
configurable: false,
get() {
console.log("get...");
return data.msg
},
// 当修改msg走set
set(newValue) {
console.log("set...", newValue);
if(newValue === data.msg){
return; // 结束函数调用
}
data.msg = newValue;
// 更新模板
document.querySelector("#app").textContent = data.msg
}
})
setTimeout(()=>{
vm.msg = "hi 123"
},2000);
</script> -->
<div id="app">hello</div>
<script>
let data = {
msg: "hello malu",
count: 18
};
let vm = {};
proxyData(data)
// proxyData可以把Data中的数据变成响应式
function proxyData(data) {
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: false,
get() {
console.log("get...");
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
console.log("set...", newValue);
if (newValue === data[key]) {
return; // 结束函数调用
}
data[key] = newValue;
// 更新模板
document.querySelector("#app").textContent = data[key]
}
})
})
}
setTimeout(() => {
vm.msg = "hi 123"
}, 2000);
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
# 2,初步了解Vue3.x响应式原理
在Vue3中,使用了Proxy处理响应式,Proxy是一种新的语法,是代理的意思,Proxy就可以代理整个数据。是ES6中出现的一个类,可以代理普通对象。兼容性肯定没有Object.definProperty兼容性好。
<div id="app">hello</div>
<script>
// 原始对象 Proxy就可以代理原始对象
let data = {
msg: "hello malu",
count: 18
};
// vm叫代理对象 给proxy指定一个目标对象
let vm = new Proxy(data, {
// target是原始对象
// key表示你获取的属性
get(target, key) {
console.log("get...");
return target[key]
},
set(target, key, newValue) {
console.log("set...");
if (target[key] === newValue) {
return;
}
target[key] = newValue;
document.querySelector("#app").textContent = target[key]
}
});
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# 3,什么是发布订阅
发布订阅:
- 发布者和订阅者没有任何关系
- 发布者和订阅者不需要知道对象存在
<script>
// 简单实现发布订阅
// 手写实现发布订阅
class EventBus {
constructor() {
// console.log("constructor...");
this.subs = {};
}
$on(eventType, fn) {
if (!this.subs[eventType]) {
this.subs[eventType] = [];
}
this.subs[eventType].push(fn)
}
$emit(eventType) {
if (this.subs[eventType]) {
this.subs[eventType].forEach(fn => {
fn();
})
}
}
}
// {eat:[fn1,fn2], "失恋":[fn1,fn2]}
let eb = new EventBus();
// 订阅 可以订阅多次
eb.$on("eat", () => {
console.log("eat事件发生了1~");
})
eb.$on("eat", () => {
console.log("eat事件发生了2~");
})
// 发布
eb.$emit("eat");
// 订阅
eb.$on("失恋", () => {
console.log("喝酒~");
})
eb.$on("失恋", () => {
console.log("睡觉~");
})
eb.$emit("失恋")
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 4,什么是观察者模式
观察者模式是基于发布订阅的,或者说,观察者模式中包含发布订阅。
观察者设计模式:
- 观察者和被观察者之间是有关系的
<script>
// 发布者
class Dep {
constructor() {
// 发布者中有一个容器,记录所有的订阅者
// 观察者模式是基于发布订阅的,一个发布者中包含了N个订阅者
// 订阅者也可以叫观察者
// 在发布者中有两个方法,一个叫addSub,用来把一个订阅者添加到subs
// 在发布者中有两个方法,一个叫notify,用来通知每一个订阅者执行update方法
this.subs = [];
}
// 添加订阅者
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// 通过所有的订阅者
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update(); // 调用订阅者的update方法
})
}
};
// 订阅者
class Watcher {
constructor() {};
// 每一个watcher中有一个update方法
// update方法,就是用来更新视图
update() {
console.log("更新视图~");
}
}
let dep = new Dep();
let watcher = new Watcher();
dep.addSub(watcher)
dep.notify();
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 二,手写MVVM
# 1,数据代理的实现原理
// myvue.js
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
// console.log("options:", options);
// this表示vm
this.$options = options || {};
this.$data = options.data || {};
this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el)
// 把data中的数据挂载到vm上,处理成响应式
this._proxyData(this.$data);
}
_proxyData(data) {
// console.log("data:",data);
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
console.log("get...");
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
if (newValue == data[key]) {
return;
}
console.log("set...");
data[key] = newValue;
}
})
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="./myvue.js"></script>
<!-- <script src="./lib/vue.2.7.14.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello vue",
count: 18,
scores: [10, 20, 30]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 2,把data中的数据处理成响应式
vue2中data中的数据是响应式的,靠的就是深度递归遍历。性能肯定没有vue3性能高。
第1小节并没有把data中的数据处理成响应式,需要把data中的数据处理成响应式数据。专门创建一个文件,叫observer.js,是专门用来处理响应式,如下:
在myvue中,使用observer.js,如下:
// observer.js
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
// console.log("data:", data);
this.walk(data);
}
// walk深度递归遍历所有的数据,处理成响应式
walk(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== "object") {
return; // 如果遍历的是一个基本类型的数据,结束递归
}
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
let that = this;
// val可能也是一个对象
this.walk(val)
// console.log(obj,key,val);
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
console.log("get...");
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) {
return;
}
console.log("set...");
val = newVal;
// 有可以你赋值的新值也可能是一个对象
// 递归处理成响应式
that.walk(newVal);
// 发出通知,更新视图~
}
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
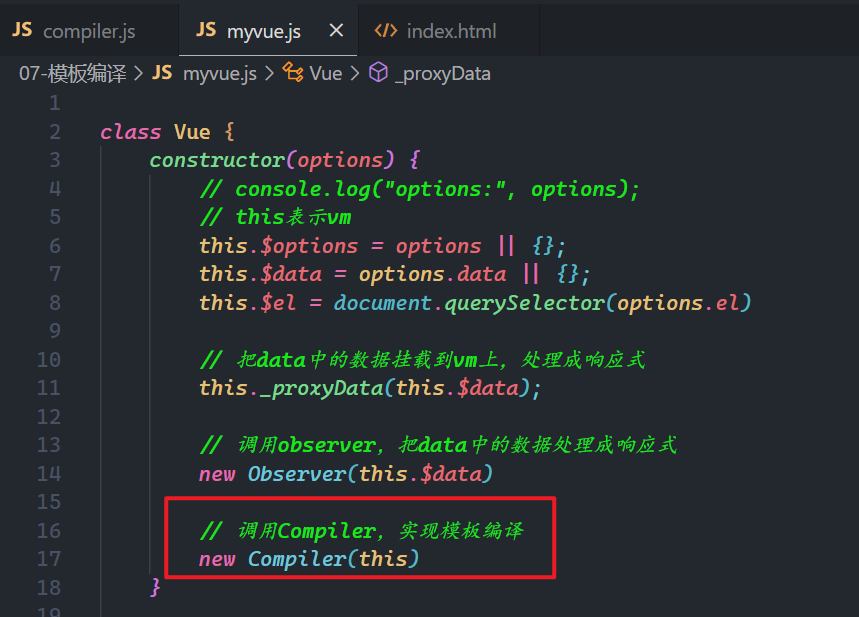
// myvue.js
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
// console.log("options:", options);
// this表示vm
this.$options = options || {};
this.$data = options.data || {};
this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el)
// 把data中的数据挂载到vm上,处理成响应式
this._proxyData(this.$data);
// 调用observer,把data中的数据处理成响应式
new Observer(this.$data)
}
_proxyData(data) {
// console.log("data:",data);
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
console.log("get...");
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
if (newValue == data[key]) {
return;
}
console.log("set...");
data[key] = newValue;
}
})
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
// index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="./observer.js"></script>
<script src="./myvue.js"></script>
<!-- <script src="./lib/vue.2.7.14.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
// msg:"hello vue",
msg: {
c: 3,
d: 4
},
count: 18,
scores: [10, 20, 30]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 3,模板编译
创建 一个文件,叫Compiler,如下:
在myvue中,使用comiler编译模板,如下:
实现compiler方法,编译小胡子语法,如下:
// compiler.js
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
// console.log(vm);
this.el = vm.$el;
this.vm = vm;
this.compile(this.el)
}
compile(el) {
// console.log(el.childNodes);
let childNodes = el.childNodes;
// console.log(Array.from(childNodes));
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
// console.log(node);
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
// console.log(node);
this.compileText(node)
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// console.log(node);
}
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) {
// 元素节点中,还有其它节点,递归遍历所有的节点
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
compileText(node) {
// console.log(node);
let reg = /\{\{(.+)\}\}/;
let value = node.textContent;
if (reg.test(value)) {
// console.log(value);
let key = RegExp.$1.trim();
// console.log(key);
// console.log(value.replace(reg, this.vm[key]));
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key]);
}
}
isElementNode(node) {
// 如果是元素节点,nodeType是1
return node.nodeType === 1;
}
isTextNode(node) {
// 如果是文本节点,nodeType是3
return node.nodeType === 3;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="./compiler.js"></script>
<script src="./observer.js"></script>
<script src="./myvue.js"></script>
<!-- <script src="./lib/vue.2.7.14.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
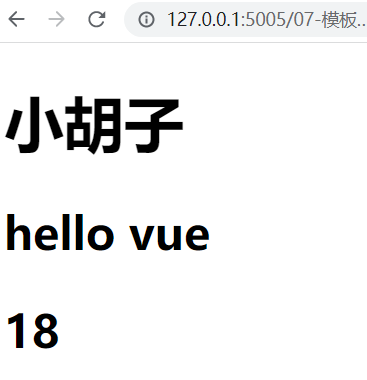
<div id="app">
<h1>小胡子</h1>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello vue",
// msg: { c: 3, d: 4 },
count: 18,
scores: [10, 20, 30]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
如果模板中有v-text,如下:
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>小胡子</h1>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
<h1>v-text</h1>
<h2 v-text="msg"></h2>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello vue",
// msg: { c: 3, d: 4 },
count: 18,
scores: [10, 20, 30]
}
});
</script>
</body>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
v-text叫属性节点,在编译元素节点时,在元素节点上是存在属性节点的,需要先编译元素节点如下:
// compiler.js
// this表示Compiler的实例
class Compiler{
constructor(vm) {
this.el = vm.$el
this.vm = vm;
this.compile(this.el);
}
// 编译模板
compile(el) {
// console.log(el.childNodes);
Array.from(el.childNodes).forEach(node => {
// console.log(node);
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
// 是文本节点
// console.log(node);
this.compileText(node);
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// console.log(node);
this.compileElement(node);
}
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) {
// console.log("有孩子~");
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
// 编译元素节点
compileElement(node) {
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
let attrName = attr.name;
// console.log(attrName);
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// v-text v-html v-show v-if
attrName = attrName.substr(2);
// console.log(attrName);
// console.log(attr.value);
let key = attr.value
this.update(node,key,attrName)
}
})
}
update(node,key,attrName) {
// console.log(attrName);
let updateFn = this[attrName + "Updater"]
updateFn && updateFn(node,this.vm[key])
}
// 处理v-text指令
textUpdater(node, value) {
// console.log(node, value);
node.textContent = value;
// console.log("textUpdater...");
}
// 处理v-model指令
modelUpdater(node, value) {
// console.log("modelUpdater...");
node.value = value;
}
// 编译文本节点
compileText(node) {
// console.log(node.textContent);
let reg = /\{\{(.+)\}\}/;
let value = node.textContent;
// console.log(value);
if (reg.test(value)) {
// console.log(value);
let key = RegExp.$1.trim();
// console.log(key);
// console.log(this.vm[key]);
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key]);
}
}
// 判断一个节点是否是文本节节点
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3;
}
// 判断一个节点是否是元素节点
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1;
}
// 判断一个属性节点是否是一个指令
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith("v-")
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
效果如下:

# 4,创建Dep发布者
// dep.js
// dep:
// 1)收集依赖,添加watcher
// 2)通知所有的watcher
// 什么时候收集依赖(添加watcher)
// 当要模板中使用数据时,收集依赖,当使用数据时会走getter
// 也就是说在getter中收集依赖,添加观察者
// 什么时候通知wacher
// 当data中的数据变化了,走setter,也就是在setter中需要通知观察者
class Dep{
constructor() {
// 存储所有的观察者
this.subs = [];
}
// 添加观察者
addSub(sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// 通知观察者
notify() {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update(); // update方法实现界面更新
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
// observer.js
class Observer {
constructor(data) {
// console.log(data);
// walk方法就是把数据处理成响应式
this.walk(data)
}
walk(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== "object") {
return;
}
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
let that = this;
console.log('-----------');
// 1)收集依赖 2)派发更新
let dep = new Dep();
// console.log(obj, key, val);
this.walk(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
console.log("get...");
// 收集依赖:就是把watcher添加到subs中
// target是静态属性 target就表示wathcer
// 现在watcher还没有
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
return val;
},
set(newVal) {
if (newVal === val) {
return;
}
console.log("set...");
val = newVal;
// newVal也可能是一个对象
that.walk(newVal)
// 派发更新: 调用watcher的update方法
dep.notify();
}
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 5,创建Watcher观察者
// watcher.js
class Watcher{
constructor(vm,key,cb) {
this.vm = vm;
this.key = key;
this.cb = cb;
// ??????
Dep.target = this;
// 更新前的旧值
this.oldValue = vm[key]
Dep.target = null;
}
update() {
let newValue = this.vm[this.key]
if (newValue == this.oldValue) {
return; // 如果新值和旧值一样,不需要更新视图了~
}
// 调用cb,去更新视图
this.cb(newValue)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// compiler.js
// this表示Compiler的实例
class Compiler {
constructor(vm) {
this.el = vm.$el
this.vm = vm;
this.compile(this.el);
}
// 编译模板
compile(el) {
// console.log(el.childNodes);
Array.from(el.childNodes).forEach(node => {
// console.log(node);
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
// 是文本节点
// console.log(node);
this.compileText(node);
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// console.log(node);
this.compileElement(node);
}
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) {
// console.log("有孩子~");
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
// 编译元素节点
compileElement(node) {
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
let attrName = attr.name;
// console.log(attrName);
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// v-text v-html v-show v-if
attrName = attrName.substr(2);
// console.log(attrName);
// console.log(attr.value);
let key = attr.value
this.update(node, key, attrName)
}
})
}
update(node, key, attrName) {
// console.log(attrName);
let updateFn = this[attrName + "Updater"]
updateFn && updateFn.call(this,node, this.vm[key],key)
}
// 处理v-text指令
textUpdater(node, value,key) {
// console.log(node, value);
node.textContent = value;
// console.log("textUpdater...");
// 创建Watcher, 当数据变化了,要更新视图
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue;
})
}
// 处理v-model指令
modelUpdater(node, value,key) {
// console.log("modelUpdater...");
node.value = value;
// 创建Watcher, 当数据变化了,要更新视图
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.value = newValue;
})
// 实现双向数据绑定
node.addEventListener("input", () => {
this.vm[key] = node.value
})
}
// 编译文本节点
compileText(node) {
// console.log(node.textContent);
let reg = /\{\{(.+)\}\}/;
let value = node.textContent;
// console.log(value);
if (reg.test(value)) {
// console.log(value);
let key = RegExp.$1.trim();
// console.log(key);
// console.log(this.vm[key]);
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key]);
// 创建Watcher, 当数据变化了,要更新视图
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue;
})
}
}
// 判断一个节点是否是文本节节点
isTextNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3;
}
// 判断一个节点是否是元素节点
isElementNode(node) {
return node.nodeType === 1;
}
// 判断一个属性节点是否是一个指令
isDirective(attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith("v-")
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
// index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="./dep.js"></script>
<script src="./watcher.js"></script>
<script src="./compiler.js"></script>
<script src="./observer.js"></script>
<script src="./myvue.js"></script>
<!-- <script src="./lib/vue.2.7.14.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>小胡子的使用</h1>
<h2>{{msg}}</h2>
<h2>{{count}}</h2>
<hr>
<h1>v-text的使用</h1>
<h2 v-text="msg" class="box"></h2>
<hr>
<h1>v-model的使用</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<input type="text" v-model="count">
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "hello vue",
// msg: { c: 3, d: 4 },
count: 18,
// scores: [10, 20, 30]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 6,总结