09-层布局
码路教育 6/15/2022
# 一、CSS层布局
标准文档流:
- 默认情况下,元素都是按照normal flow(标准流、常规流、正常流、文档流【document flow】)进行排布
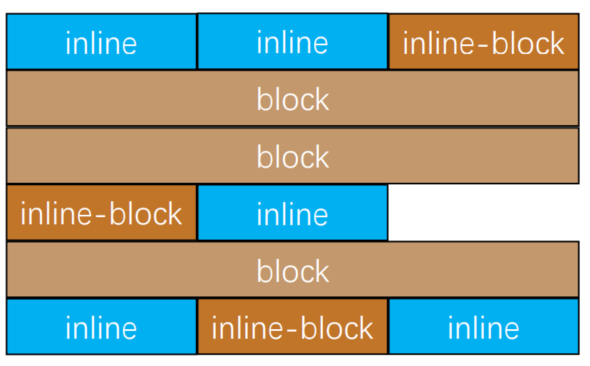
- 块级元素独占一行 → 垂直布局
- 行内元素/行内块元素一行显示多个 → 水平布局
- 默认情况下,互相之间不存在层叠现象
- 在标准流中,可以使用margin、padding对元素进行定位,其中margin还可以设置负数
- 设置一个元素的margin或者padding,通常会影响到标准流中其他元素的定位效果,不便于实现元素层叠的效果
- 如果我们希望一个元素可以跳出标准文档流,可以通过position属性来进行设置
- 可以让元素自由的摆放在网页的任意位置
- 一般用于盒子之间的层叠情况,定位之后的元素层级最高,可以层叠在其他盒子上面
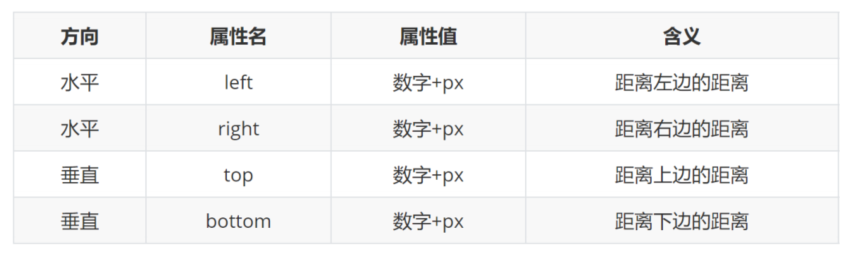
- 定位方式 和 设置偏移值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
标准文档流:
你写的任何一个盒子,都在是标准文档流中进行排布的。
类似一个国家,有很制度,把盒子分成三类:
1)块级盒子 独占一行
2)行内级盒子 并排显示
3)行内块级盒子 并排显示
默认情况下,标准文档流中的盒子,不会层叠在一起
在标准文档流中,对盒子进行定位,可能通过margin和padding动盒子的位置,并且margin可以为负值
在标准文档流中,过margin和padding动盒子的位置,会影响到其它盒子。
如果想让一个盒子在网页上的任何位置,不影响其它盒子,此时按标准文档流进行布局就不OK了。
层布局:
层布局,就可以让盒子层叠在一起。通过定位实现。
定位分三次:
1)相对定位
position:relative; left right top bottom
2)绝对定位 完全脱标
position:absolute; left right top bottom
3)固定定位 完全脱标
position:fixed; left right top bottom
-->
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
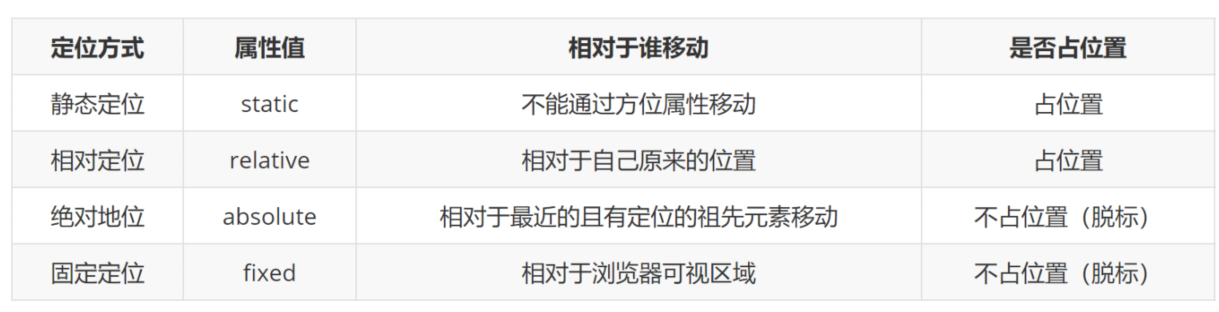
静态定位 - static:
- 静态定位是默认值,就是之前认识的标准流,元素按照normal flow布局
- left 、right、top、bottom没有任何作用
- 说白了,就是不定位
- 之后说的定位不包括静态定位,一般特指后几种:相对、绝对、固定
相对定位 - relative:
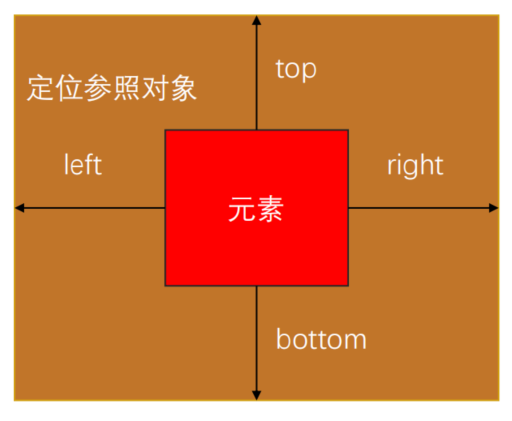
- 相对于自己之前的位置进行移动
- 可以通过left、right、top、bottom进行定位
- 定位参照对象是元素自己原来的位置
- left、right、top、bottom用来设置元素的具体位置
- 在页面中占位置,没有脱标
- 应用场景:1)配合绝对定位组CP(子绝父相) 2)在不影响其他元素位置的前提下,对当前元素位置进行微调
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.father{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: gold;
}
.son{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: skyblue;
/* 相对定位 */
/* relative 是相对的意思 */
/* 相对定位的参考点:原本的位置 */
position: relative;
/* top: 50px;
left: 50px; */
bottom: 30px;
/* right: 50px; */
}
/*
相对定位特点:
1)参考点:自己本应该出现的位置
2)需要通过 left right top bottom 设置偏移量 要么使用一个,要么使用二个
3)相对定位的元素并没有脱标,原本的位置,还是被占用着
4)应用场景:A)局部位置调整 B)作为绝对定位的参考点
*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
<div class="son2">son2</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
相对定位的应用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.box{
height: 489px;
background-color: #f00;
}
.box img{
/* 相对定位 */
position: relative;
/* top,left,right,bottom可以设置负值 */
left:-960px;
/* 这里的50%是相对于box的50% */
margin-left: 50%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<img src="./images/mhxy.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
固定定位 - fixed:
- 元素脱离normal flow(脱离标准流、脱标)
- 可以通过left、right、top、bottom进行定位
- 相对于浏览器进行定位移动
- 固定定位元素的特点
- 可以随意设置宽高
- 宽高默认由内容决定
- 不再受标准流的约束
- 不再严格按照从上到下、从左到右排布
- 不再严格区分块级、行内级,块级、行内级的很多特性都会消失
- 脱标元素内部默认还是按照标准流布局
- 可以随意设置宽高
5.应用场景:
- 让盒子固定在屏幕中的某个位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<!--
固定定位:
1)完全脱离标准文档流,叫脱标
2)需要通过 left right top bottom 设置偏移量 要么使用一个,要么使用二个
3)参考点是整个浏览器的视口
4)一个女盒子会直接变成男盒子
5)固定定位的元素内部还是按标准文档流进行布局
-->
<style>
span{
position: fixed;
bottom: 10px;
right: 10px;
/* 出国的盒子,就不再严格区分男盒子,女盒子,人妖盒子 */
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: gold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>
<i>1</i>
<i>2</i>
<i>3</i>
</span>
<h1>我是一个H1</h1>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
固定定位案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box{
position: fixed;
right: 30px;
bottom: 30px;
}
.box .item{
width: 80px;
height: 40px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
background-color: brown;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.box .item:hover{
background-color: #f00;
}
.top{
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="item top">顶部</div>
<div class="item bottom">反馈</div>
</div>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
绝对定位 - absolute:
- 在页面中不占位置,元素脱离normal flow(脱离标准流、脱标)
- 定位参照对象是最邻近的定位祖先元素
- 如果找不到这样的祖先元素,参照对象是视口
- 定位元素(positioned element)是指position值不为static的元素
- 子绝父相:在绝大数情况下,子元素的绝对定位都是相对于父元素进行定位
- 子元素相对于父元素进行定位,又不希望父元素脱标
- 子元素相对于父元素进行定位,又不希望父元素脱标
- 如果希望绝对定位元素的宽高和定位参照对象一样,可以给绝对定位元素设置以下属性
- left: 0、right: 0、top: 0、bottom: 0、margin:0
- left: 0、right: 0、top: 0、bottom: 0、margin:0
- 如果希望绝对定位元素在定位参照对象中居中显示,可以给绝对定位元素设置以下属性
- left: 0、right: 0、top: 0、bottom: 0、margin: auto
- 另外,还得设置具体的宽高值(宽高小于定位参照对象的宽高)
- left: 0、right: 0、top: 0、bottom: 0、margin: auto
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
.father{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: gold;
margin: 100px auto;
/* 这一行代码不再是相对定位,是设置参考点 */
position: relative;
}
.son1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
/* 绝对定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
z-index: 100;
}
.son2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
/* 绝对定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 80px;
left: 80px;
z-index: 80;
}
.son3{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
/* 绝对定位 */
position: absolute;
top: 110px;
left: 110px;
z-index: 50;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
绝对定位:
1)完全脱标
2)需要通过 left right top bottom 设置偏移量 要么使用一个,要么使用二个
3)参考点 需要我们后动设置 如果不设置,最终以body作为参考点
4)设置参考点:position:relative; position:fixed; position:absolute;
5)大部分情况下,设置参考点是通过 position:relative;
6)大部分情况下,会把参考点设置到父元素上,子绝父相
7)通过z-index可以改变层叠顺序 值越大,越靠前
-->
<div class="father">
<div class="son1">son1</div>
<div class="son2">son2</div>
<div class="son3">son3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
z-index:
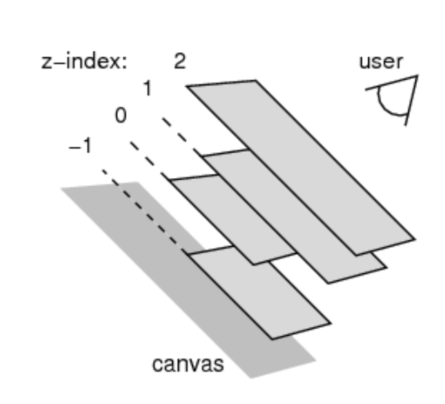
- z-index属性用来设置定位元素的层叠顺序(仅对定位元素有效)
- 取值可以是正整数、负整数、0
- 如果是兄弟关系
- z-index越大,层叠在越上面
- z-index相等,写在后面的那个元素层叠在上面
- z-index越大,层叠在越上面
- 如果不是兄弟关系
- 各自从元素自己以及祖先元素中,找出最邻近的2个定位元素进行比较
- 而且这2个定位元素必须有设置z-index的具体数值
- 各自从元素自己以及祖先元素中,找出最邻近的2个定位元素进行比较
使用绝对定位实现水平垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
.father{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: gold;
position: absolute;
top:50%;
left:50%;
margin-left: -250px;
margin-top: -250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
</div>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
粘性定位 - sticky:
- 可以看做是相对定位和固定定位的结合体;
- 它允许被定位的元素表现得像相对定位一样,直到它滚动到某个阈值点;
- 当达到这个阈值点时, 就会变成固定定位;
- sticky是相对于最近的滚动祖先包含视口的
position值对比: